Australia’s manufacturing capabilities will play a key role in the country’s economic rebuild post COVID-19.
This is not news to the ANSTO Silicon team, who have been supporting high-end manufacturing industries all over the world since the 1990s.
Utilising ANSTO’s OPAL reactor to improve the electronic properties of irradiated silicon, the business has established Australia as the country which produces one of the most high-quality materials used for renewable energy in the electronic industry.
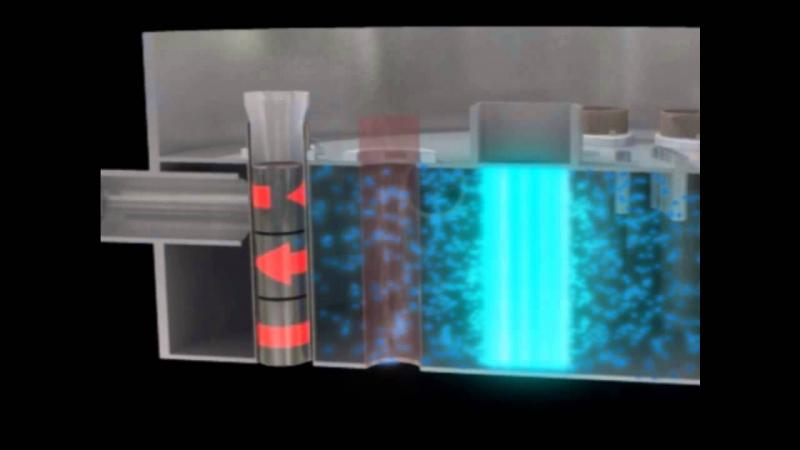
Irradiating silicon through a process called Neutron Transmutation Doping (NTD), changes its properties by introducing phosphorous, an element which improves its conductivity, or capacity to conduct electricity.
Silicon is used in manufacturing high-tech electronic devices for a wide range of green technologies, such as hybrid and electric vehicles, high-speed trains, wind turbine systems, power grid infrastructure and robotics, and industrial automation equipment among other applications.
Today, ANSTO is the world’s leading producer of the highest quality NTD irradiated silicon with the greatest demand coming from China, Europe and Japan. The OPAL reactor meets global customer demand due to its capacity, efficiency and output.
Throughout COVID-19, the team at ANSTO’s OPAL reactor and within the Silicon business minimised disruption to production by continuing to operate in order to fulfil product orders.
To produce NTD silicon, high purity silicon ingots supplied by customers are placed in the reactor pool for irradiation with neutrons over a period of time. After they have been removed, cooled to allow for sufficient radiation decay and become safe to handle, they are cleaned, packaged and sent back to customers.
ANSTO’s market share is currently at 58% - which represents a larger global market share than all their competitors combined. Since 2013, silicon production has increased from 20% to 58% in 2019.
ANSTO’s OPAL reactor is one of a small number of reactors with the capacity to produce commercial quantities of radioisotopes. This capacity, combined with the open pool design, the use of low enriched uranium fuel and the wide range of applications, places OPAL amongst the best research reactors in the world.
“ANSTO’s state-of-the-art OPAL multipurpose reactor is one of the most reliable research reactors in the world,” says Group Executive of the Nuclear Precinct, Pamela Naidoo-Ameglio.
“OPAL enables the application of nuclear science to improve human health, save lives, protect the environment and, through our Silicon irradiation business, make a significant contribution to the high-end electronics industry.”
“We pride ourselves on the service and expertise we offer our customers. Our focus on reliability, product quality and excellent service ensures customers from all over the world choose ANSTO,” says Tanya Karma, Business Manager Silicon Irradiation.
“Our utilisation of the OPAL reactor is just one example of how nuclear technology delivers high-end solutions in advanced manufacturing. We are seeing the benefits of silicon production in sustainable energy reliability and efficiency all over the world.”