Published on the 14th April 2023 by ANSTO Staff
Conservators and curators from the Art Gallery of New South Wales have used an advanced imaging technique at the Australian Synchrotron to gain more information about an underpainting in a famous Renaissance portrait of Cosimo I de’ Medici, Grand Duke of Tuscany from 1537 to 1569.
The painting, Cosimo I de’ Medici in armour, by Agnolo di Cosimo, known as Bronzino , is one of at least 25 known portraits of the Duke in armour and the only painting by the Italian mannerist painter in an Australian collection.
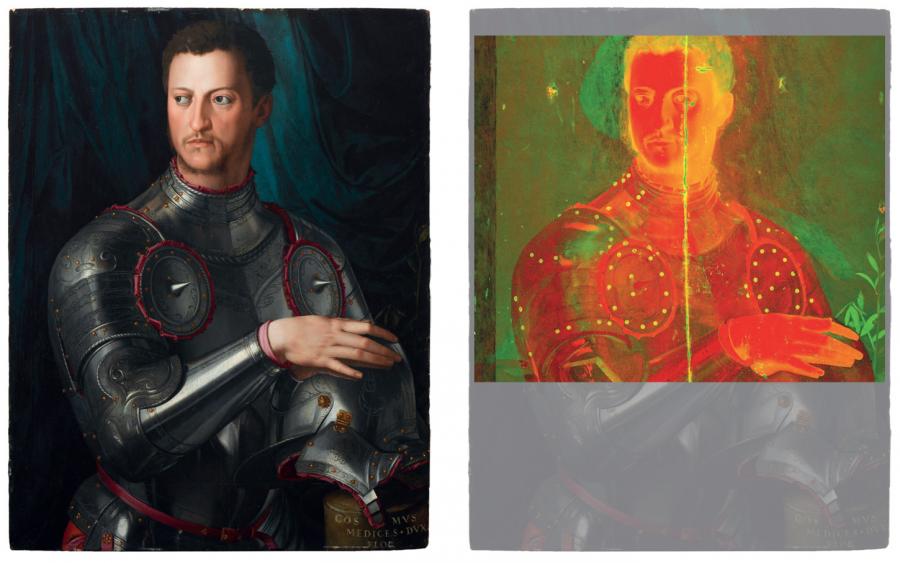
Art Gallery of NSW painting conservators Simon Ives, and Paula Dredge (now at The University of Melbourne) and curator of international art Anne Gérard-Austin, used the X-ray fluorescence (XFM) microscopy instrument to scan the portrait with the assistance of senior instrument scientist Dr Daryl Howard.
Co-author Dr Howard, who has considerable expertise with investigations of precious works of art, said, “XFM is now an important tool for art historians and museum curators as it can detect and map metals in paint pigments non-invasively.”
As reported in an article recently published in the prestigious art journal, The Burlington Magazine, most of the metallic elements in pigments can potentially be imaged with the technique.
[The January issue of the Burlington Magazine with the article can be downloaded]
Renaissance artists used expensive paints containing minerals in some parts of their paintings, which can be identified by XFM.
The elements mapped by XFM in the painting included mercury (present in the red pigment vermillion, copper (found in azurite), tin (correlated with the use lead tin yellow), iron, (present in a range of ochres) and manganese (in umber) as well as trace elements, notably arsenic, in these pigments derived from mineral deposits.
The distribution of elements was mapped across the painting producing single greyscale images that represent the distribution of individual elements. Tonal differences indicate variable concentrations of elements.
The existence of a figure under the portrait of Duke Cosimo had been revealed in the early 1980s from an X-ray conducted by American art historian Robert Simon (who later famously discovered Leonardo da Vinci’s Salvator Mundi). The Art Gallery of NSW acquired the Bronzino painting in 1996, but it was still unclear if the figure underneath was an earlier version of the duke.
The recent investigation established that the NSW Art Gallery’s portrait of Duke Cosimo was the earliest or ‘prime autograph version’ of the three-quarter length composition, following the primary half-length version of the portrait held in the Uffizi in Florence.
The authors also proposed that the image beneath may represent the early thoughts for a painting completed on another panel, Portrait of a young man, now in the Nelson-Atkins Museum in Kansas.
Dr Howard said the synchrotron XFM beamline was experienced in handling invaluable art works, including Portrait of a Woman by Edgar Degas and The North Wind by Australian artist Frederick McCubbin.