Radon is a naturally-occurring radioactive trace gas of terrestrial origin.
As an unambiguous tracer of terrestrial influence on air mass composition, radon is an essential component of baseline studies for:
- the selection of least terrestrially perturbed marine air masses
- tracing and analysis of air mass history and fetch;
- calibration/constraint of regionally-integrated emission estimates for important distributed trace gases; and
- an evaluation of transport and mixing schemes in climate and chemical transport models.
The Radon Analytical Laboratory operates a comprehensive suite of instrumentation for the monitoring and analysis of natural radioactivity resulting from radon (222Rn). This short-lived noble gas is an independent signal, generated from the land surface, that can be used to differentiate baseline greenhouse gases and pollutants from recent point contributions. In high concentrations that may accumulate in enclosed spaces or buildings, it presents a health hazard.
The facility’s capabilities include portable monitors for indoor/outdoor use (commercial AlphaGUARD monitors, and 100L ANSTO monitors), and 3 sizes of outdoor monitors (200, 700 and 1500L), with increasing sensitivities to radon at 30-minute temporal resolution.
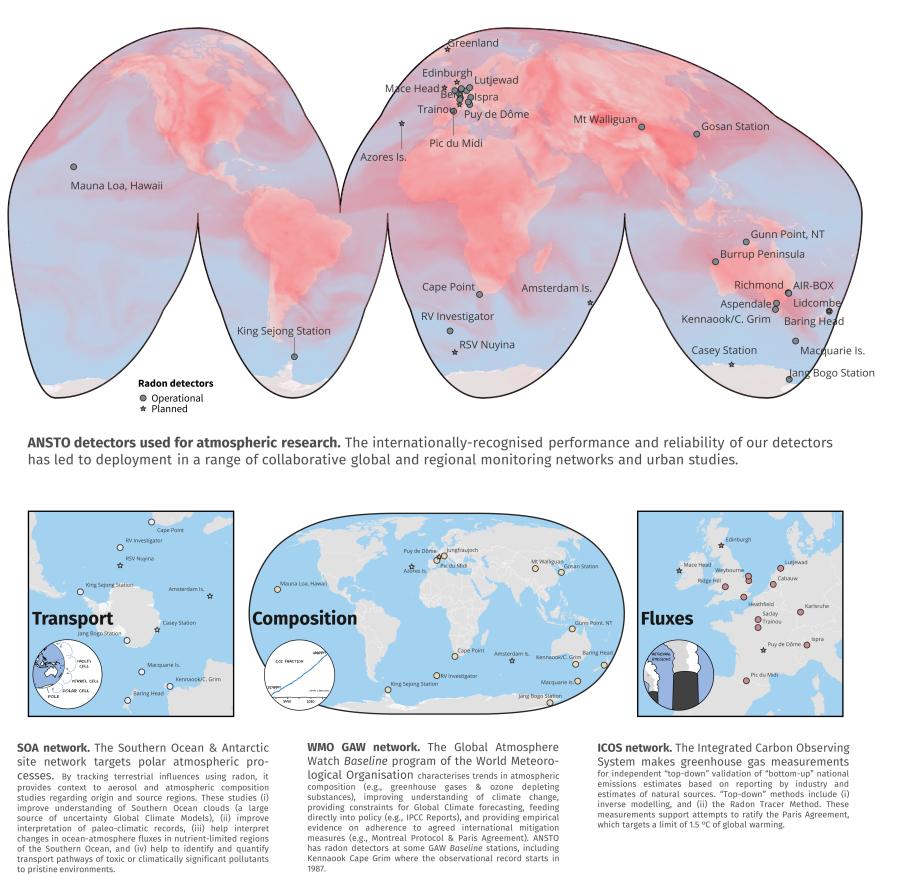
ANSTO radon monitors are currently being used at almost 40 sites worldwide, including Kennaook/Cape Grim (Tasmania), Macquarie Island, Cape Point (South Africa), Mauna Loa Observatory (Hawaii, USA), Gosan Station (Jeju Island, South Korea), Jungfraujoch (Swiss Alps), King Sejong Station (Antarctica), Mt Waliguan (Tibet), and aboard the Australian National Marine Facility RV Investigator.
A complete list of operational sites, as well as a list of their primary network objectives, is listed below. The red hue represents a snapshot of radon concentration in the atmosphere, modelled at the ANSTO HPC facility using the GEOS-Chem model.

Dual flow loop, two-filter radon detector
ANSTO's unique technology for highly sensitive measurements of atmospheric radon is recognised by the World Meteorological Organisation as the best in the world for global and atmospheric compositional baseline studies.
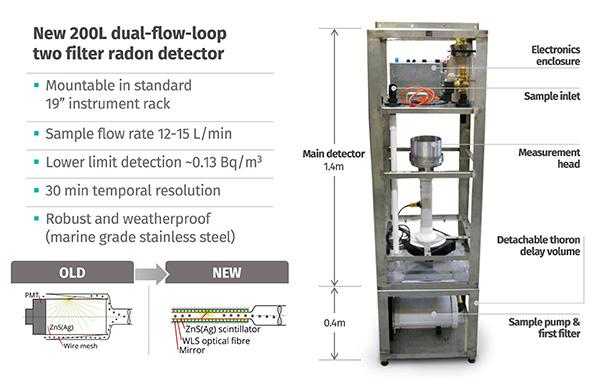
Three models (200, 700 and 1500 L) of semi-portable detectors are available for outdoor, continuous, hourly monitoring of ambient radon in air. These detectors, which can be maneuvered by 2-4 persons (<3m long; 80 - 120 kg), can be deployed to most field sites for either short-term (several weeks), or semi-permanent, monitoring.
